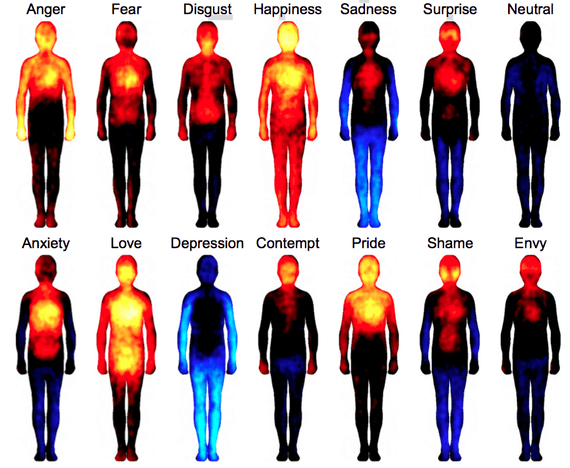
A new set of experiments asked participants to read short stories or watch movies and then “color in the areas of their body where sensations became stronger (the red and yellow) or weaker (blue and black) when they felt a certain way”:
The mapping exercise produced what you might expect: an angry hot-head, a happy person lighting up all the way through their fingers and toes, a depressed figurine that was literally blue (meaning they felt little sensation in their limbs). Almost all of the emotions generated changes in the head area, suggesting smiling, frowning, or skin temperature changes, while feelings like joy and anger saw upticks in the limbs—perhaps because you’re ready to hug, or punch, your interlocutor. Meanwhile, “sensations in the digestive system and around the throat region were mainly found in disgust,” the authors wrote. It’s worth noting that the bodily sensations weren’t blood flow, heat, or anything else that could be measured objectively—they were based solely on physical twinges subjects said they experienced. The correlations between the subjects’ different body maps were strong—above .71 for each of the different stimuli (words, stories, and movies). Speakers of Taiwanese, Finnish, and Swedish drew similar body maps, suggesting that the sensations are not limited to a given language.
So what are we seeing in these illustrations? The authors note that, measured physiologically, most feelings only cause a minor change in heart rate or skin temperature—our torsos don’t literally get hot with surprise. Instead, the results likely reveal subjective perceptions about the impact of our mental states on the body, a combination of muscle and visceral reactions and nervous system responses that we can’t easily differentiate. Feeling jealous may not truly make us red in the face, for example, but we certainly might feel like it does.