Lauren Slater investigates exotic pet ownership across the country:
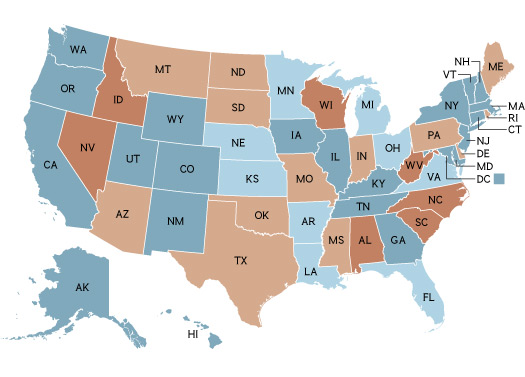
Privately owning exotic animals is currently permitted in a handful of states with essentially no restrictions: You must have a license to own a dog, but you are free to purchase a lion or baboon and keep it as a pet. Even in the states where exotic-pet ownership is banned, “people break the law,” says Adam Roberts of Born Free USA, who keeps a running database of deaths and injuries attributed to exotic-pet ownership:
In Texas a four-year-old mauled by a mountain lion his aunt kept as a pet, in Connecticut a 55-year-old woman’s face permanently disfigured by her friend’s lifelong pet chimpanzee, in Ohio an 80-year-old man attacked by a 200-pound kangaroo, in Nebraska a 34-year-old man strangled to death by his pet snake. And that list does not capture the number of people who become sick from coming into contact with zoonotic diseases.
The term exotic pet has no firm definition; it can refer to any wildlife kept in human households—or simply to a pet that’s more unusual than the standard dog or cat. Lack of oversight and regulation makes it difficult to pin down just how many exotics are out there. “The short answer is, too many,” says Patty Finch of the Global Federation of Animal Sanctuaries. It’s estimated that the number of captive tigers alone is at least 5,000—most kept not by accredited zoos but by private owners. And while many owners tend to their exotic pets with great care and at no small expense, some keep their pets in cramped cages and poor conditions.